chest compression test wiki|How to Perform CPR: Hands : discount store Learn what chest compressions are, their importance in CPR, and how to perform them correctly to help save lives during a cardiac emergency. webCOVID-19: orientações para as festas de fim de ano. Com a aproximação das festas de fim de ano, as famílias passam cada vez mais a pensar em como serão as comemorações .
{plog:ftitle_list}
6.7k 0 11 18. HENTAI X. 25 Jan, 05:33. for everyone. the first time acces. 💧to a new private channel. ⚡️with long videos >10-15min. ⚡️new content every 6 hours. ⚡️2 .
CPR – or Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation – is an emergency lifesaving procedure performed when the heart stops beating. Immediate CPR can double or triple chances of survival after cardiac arrest. The American Heart Association .
Learn what chest compressions are, their importance in CPR, and how to perform them correctly to help save lives during a cardiac emergency.
Although the use of mouth-to-mouth ventilation as a resuscitative technique dates back virtually to the beginning of recorded history, it seems to have fallen out of favor in the late 19th century with the widespread adoption of Silvester's method (the chest-pressure and arm-lift technique). Silvester's method remained the most widespread method of resuscitation from its description in . Perform 30 chest compressions. Press down with both hands directly over the breastbone to perform a compression, which helps the heart beat. Chest compressions are more critical for correcting abnormal heart . Method 1. Using Hands-Only CPR for Adults and Teens. Download Article. 1. Examine the scene for any obvious hazards. In some cases, it may not be safe to perform .
Chest compressions. To do chest compressions, place the lower palm of your hand over the center of the person's chest and your other hand on top of your first hand. Keep your elbows straight. Place your shoulders directly . Chest compressions involve pushing hard and fast in the center of the chest. If you've had training, you can use chest compressions, clear the airway, and do rescue . Steps for CPR with breaths: adults. CPR with breaths: Steps for children. CPR with breaths: Steps for infants. CPR and AED training. What is CPR? Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a lifesaving.CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) is a way to save the life of someone who’s in cardiac arrest (when their heart can’t pump blood) by attempting to restart their heart. It’s a fairly simple .
What is CPR
LUCAS 2 device demonstrated on a mannequin. The Lund University Cardiopulmonary Assist System (LUCAS) device provides mechanical chest compressions to patients in cardiac arrest.It is mostly used in emergency .Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like You arrive on the scene to find CPR in progress. Nursing staff report the patient was recovering from a pulmonary embolism and suddenly collapsed. Two shocks have been . Introductory background. The lung is encased by the chest wall, a multi-part structure comprised of the rib cage and abdomen. Considered independently, these interlocked components of the respiratory system have different innate mechanical properties [].Quite apart from gravity, the local flexibility of the chest wall varies markedly from site to site; dorsal .
What Are Chest Compressions?
To do chest compressions, place the lower palm of your hand over the center of the person's chest and your other hand on top of your first hand. Keep your elbows straight. Place your shoulders directly above your hands. Using your upper body weight, push straight down on the chest about 2 inches (5 centimeters). Do not push down more than 2.4 .Patient Care.It is important that those responsible for the personal care of a patient who has chest tubes inserted understand the basic mechanics of inflation and deflation of the lung, and the purpose of the tubes and their location in each patient.In some cases one tube is inserted higher in the thorax (usually in the 2nd intercostal space) to remove air, and a second tube is placed .
Chest compressions recreate this pumping motion so the blood circulates to vital organs and the rest of the body. The compression rate is the number of compressions you should perform in 1 minute . Place your hands on the center of their chest with one hand on top of the other. Center your weight over you hands. Perform chest compressions to help restore blood flow to vital organs.Use your body weight to firmly press at least 2 inches deep (but no deeper than 2.4 inches) at a rate of about 100 to 120 compressions per minute.
Start chest compressions. Do not delay chest compressions if the pulse cannot be felt within 10 seconds. Just do your best. If you stand still and do nothing, the person is going to expire. 4. Chest compressions. A person present on the site, whether trained or not, should start chest compressions to the victim suffering cardiac arrest. Every time you do a chest compression, push the chest down by 5 to 6 cm (about 2 inches). Repeat the compressions at a fast rate of about two compressions per second (100 to 120 compressions per minute). Make sure that your arms remain stretched (don’t bend at the elbows), or they will soon get tired.Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly imaging techniques) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints, blood vessels, and internal organs, to measure some characteristics (e.g., distances and velocities) or to generate an .
Compression Depth. The depth of compressions is crucial for ensuring that blood is effectively circulated through the body: Adults: Compress the chest at a depth of at least 2 inches (5 cm) but not more than 2.4 inches (6 cm).This depth helps generate enough pressure to maintain blood flow while minimizing the risk of injury. To perform CPR, place the heel of one hand in the center of the chest. Place the other hand on top and interlock the fingers. Push straight down hard and fast at 100 to 120 beats a minute. . Chest compressions might require opening or cutting away someone's bulky clothing or removing a bra to reach the middle of their chest or apply AED pads .Adults need 30 chest compressions, followed by 2 breaths. Continue this CPR cycle until help arrives, or they start breathing. Chest compressions are the most important part of CPR. Start chest compressions as soon as possible after calling for help. D: Defibrillation: Attach an Automated External Defibrillator (AED) to the person if one is .
These 11 workout compression shirts from brands like Under Armour, Lululemon, and more are designed to wick sweat, improve blood flow, and enhance recovery. Make sure you allow their chest to come all the way back up between compressions. People who have CPR training can pause compressions to give the person two mouth-to-mouth rescue breaths for every 30 compressions (about 20 seconds or so). Keep doing chest compressions and giving rescue breaths in a cycle until the person revives or . Air traveler numbers are predicted to reach 4.0 billion in 2024. Between 1/15,000–50,000 passengers will experience acute medical problems inflight with cardiac arrests requiring cardiopulmonary .
take impact test certificate online free
Chest compressions involve pushing hard and fast in the center of the chest. If you've had training, you can use chest compressions, clear the airway, and do rescue breathing. Rescue breathing helps get oxygen to the lungs for a person who has stopped breathing. To keep your skills up, repeat the CPR training every two years.
The term ‘thoracic outlet syndrome’ describes compression of the neurovascular structures as they exit through the thoracic outlet (cervicothoracobrachial region). . the spine is gently flexed as far as possible moving the ear toward the chest. A test is considered positive when the lateral flexion movement is blocked. Test: Sensitivity . Background. Cardiac arrest is a severe, life-threatening condition and remains a leading cause of out-of-hospital death worldwide. Adult patients who experience out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) have a low survival rate, approximately 10.4%, and only 8.2% of them survive and have a good functional status [].Standard cardiopulmonary resuscitation (STD . Intercostal neuralgia is characterized by neuropathic pain in the distribution of affected intercostal nerve(s) (along the ribs, chest, or abdomen) that commonly manifests as a sharp, aching, radiating, burning, or stabbing pain and may be associated with paresthesia such as numbness and tingling. The pain may be intermittent or constant and typically presents .
Chest compressions are hard work and after 100 chest compressions or if you become fatigued, it is recommended that you switch chest comrpessions with someone nearby. To transfer chest compressions effectively, there must .
Drs. Kouwenhoven and Knickerbocker worked with cardiac surgeon, Dr. James Jude, to test this life sustaining theory on many patients for over a year before announcing the results of their discovery: Chest compressions could maintain 40% of a patient’s normal circulation when their heart had stopped beating.Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a condition in which there is compression of the nerves, arteries, or veins in the superior thoracic aperture, the passageway from the lower neck to the armpit, also known as the thoracic outlet. [1] There are three main types: neurogenic, venous, and arterial. [1] The neurogenic type is the most common and presents with pain, weakness, .
Introduction Cardiac arrest is a leading cause of death in industrialised countries. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) guidelines follow the principles of closed chest compression as described for the first time in 1960. Mechanical CPR devices are designed to improve chest compression quality, thus considering the improvement of resuscitation .
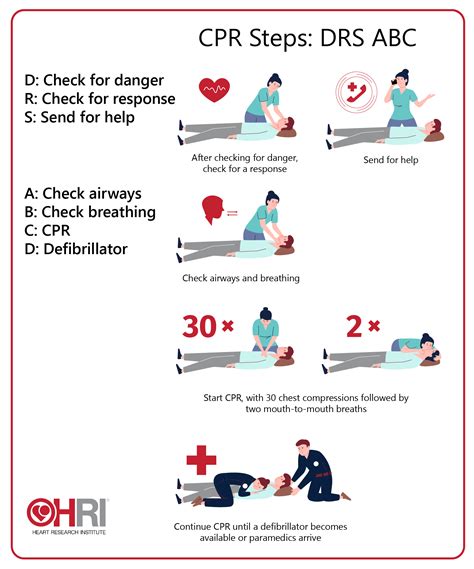
Enhance your CPR skills with our CPR practice test, reflecting real emergency scenarios. Covering chest compressions, rescue breaths, AED use, and more. Home; . The test covers all aspects of CPR, including chest compressions, rescue breaths, AED use, and other relevant procedures. It is challenging enough to assess your ability to perform .Opening the airway with a head tilt-chin lift maneuver Looking, listening and feeling for breathing Perform chest compressions to support circulation in those who are non-responsive without meaningful breaths. ABC and its variations are initialism mnemonics for essential steps used by both medical professionals and lay persons (such as first aiders) when dealing with a patient.
Rescuers should perform chest compressions for all ages at a rate of 100 to 120 compressions per minute (almost 2 compressions/second). 1,2,4,9,11 [CoSTR 2015/2020strong recommend, ation, very-low-certainty evidence] This does not imply that 100-120 compressions will be delivered each minute since the
How to Perform CPR: Hands
webIDS - Instituto de Diagnósticos. Resultados. website ou app. Instruções. para os Exames. Conheça nossas Unidades. Notícias e Eventos. veja mais postagens. Convênios que .
chest compression test wiki|How to Perform CPR: Hands